46submissions
Finished
46 Positive Science Posts To Remind Us Of All The Good That’s Happening In The World
Positive news is underrated! It’s easy to get into the habit of thinking the world’s going downhill. Sure, it’s not all sunshine and rainbows all the time, but objectively speaking, there’s a lot to be happy about and proud of. However, we’re hard-wired to prioritize negative news, so we can all use a reminder about all the good things out there.
Case in point, the popular ‘Upworthy Science’ account on Instagram posts updates about all the wonderful progress happening in the scientific world, both on a global and local scale. We’ve collected some of the most uplifting bits of science news they’ve featured to share with you, Pandas. Scroll down to check them out!
More info: Instagram | UpworthyScience.com
This post may include affiliate links.
Chances are you’ve never heard of Guinea worm disease, a parasitic sickness which often causes infection, lock jaw, joint infections, and permanent disability. Decades ago, the disease afflicted 3.5 million people each year — but thanks to the heroic efforts of Dr. Donald Hopkins and others, there are currently just 28 cases of Guinea worm disease worldwide. Hopkins, born in Miami in 1941, grew up in poverty, the seventh of ten children. On a study-abroad trip to Egypt, Hopkins saw the devastating effects of disease on the global population and decided to pursue medicine. After graduating medical school at the University of Chicago (the only black student in his graduating class), Hopkins went on to work with the CDC to eradicate smallpox in Sierra Leone. At the time (1967) Sierra Leone had the highest smallpox rate in the world. Hopkins’ unique vaccination strategies helped Sierra Leone report their last case of smallpox just two years later. In the early 1980s, Hopkins set out to destroy another debilitating disease — Guinea worm. The disease, caused by unclean drinking water, affected millions across Africa at the time, but Hopkins was undeterred: “When people said to me, ‘You’re not going to be able to eradicate Guinea worm disease,’ I had heard all of that about smallpox. So I just brushed it off.” For decades, Hopkins (working alongside former president Jimmy Carter) has traveled across Africa and battled cultural differences, political rivalries, bad roads, and dilapidated health systems to bring clean water and larvicide to struggling populations. With just 28 cases worldwide in 2021, Hopkins and his team are on the verge of declaring victory — but the 79-year-old scientist won’t retire until the disease is completely gone: “I’ve got the tiger by the tail and I can’t let go.”
By banning the use and new production of CFCs, the Montreal Protocol eliminated a significant contributor to climate change. It’s estimated that these efforts avoided a temperature increase of as much as 2.5 degrees. We love to see people working together to use science for the good of humanity
A 13-year-old girl named Alyssa has been totally cleared of a deadly, incurable cancer after doctors used a technology called “base editing” to build her a new, living medication. Alyssa was diagnosed with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in May of last year. With this particular type of cancer, the body’s T-cells—which are designed to fight off infections—instead mutate and multiply out of control. Despite trying chemotherapy and a bone marrow transplant, Alyssa’s cancer still persisted, and earlier this year she was given just months to live. In an amazing feat of science, however, a team of doctors and scientists were able to use an experimental new tool called “base editing” to engineer brand new T-cells—ones specially equipped to hunt and kill off Alyssa’s cancerous T-cells. After just one round of this new treatment, Alyssa has been declared cancer-free, and can now spend Christmas with her family
An eight-year-old girl named Xochitl Guadalupe Cruz is saving the environment and helping low-income families in her village, all at the same time. Alongside her father, Cruz wanted to find a way to lessen her community’s reliance on cutting down trees for firewood. Hot water, however, is a necessity, Cruz said in a video. “In San Cristobal, it’s very cold most of the year. If people shower with cold water they can get sick with respiratory illnesses and have to go to the doctor.” So Cruz made a heater from recycled objects like black bottles, black nylon, and recycled glass. When the water is filtered into the heater, it can warm ten liters of water to anywhere between 95 and 115 degrees, even in cold weather. At age nine, Cruz won the Instituto de Ciencia Nuclear de Universidad Nacional Autonomy de Mexico (ICN-UNAM) Women’s Recognition Award, making her the first child to ever do so. She’s now planning to build a larger water heater for even more neighbors to use
When Hadiyah-Nicole Green was in her early twenties, she received some news that would change her life forever: Her aunt (pictured here), who had raised her since the age of four, had terminal cancer. Fearing the effects of chemo and radiation, her aunt chose instead to die without treatment. Three months after her aunt's death, her uncle was diagnosed with cancer as well – and though he chose to undergo treatment, the chemotherapy and radiation made him seriously ill and were ultimately ineffective. He died less than a year later. Though losing her aunt and uncle was devastating, Green decided she would dedicate her life to fighting cancer in their memory – and also to make cancer treatments with less side effects. Green got a master's degree and then a PhD in physics, and turned her interest to lasers. She theorized that lasers could be use to precisely kill cancer cells while leaving the healthier cells intact. She spent the next three years developing a laser technology that uses nanoparticles to destroy cancer cells. Green's persistence paid off: she soon became the first person to use nanoparticles to cure cancer in mice, with no observable side effects. Her ultimate goal is to make this treatment available to human beings. Green is now hard at work trying to bring her technology to human trials. To that end, she has established the Ora Lee Smith Cancer Research Foundation (named after her late aunt), a non-profit to support her cancer research. Once her treatment is developed, Green wants to provide the treatment through her non-profit organization rather than sell it to a pharmaceutical company, enabling it to be affordable and accessible to everyone.
Billionaire entrepreneur Mark Cuban (you might have seen him on the TV show “Shark Tank”) launched an online pharmacy that is poised to change lives for the better. Cuban’s new venture, called the Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company (MCCPDC), offers “huge” savings on generic prescription medication – some that retail for thousands of dollars each month.
According to a press release from the company, MCCPDC provides medication at cost with a flat 15% margin for pharmacist fees. In this way, medication for a variety of health concerns such as cancer can be provided to consumers for just a fraction of the retail cost. Gleevac, for instance, which can cost more than $9,000 for one month’s supply, can be purchased on the MCCPDC website for just $47 – no insurance necessary. This news will no doubt come as a relief to millions of Americans who, according to a Gallup poll taken in September 2021, are unable to pay for at least one of their prescription medications due to rising costs. Here’s to Cuban, who’s doing his part to make medicine accessible to everyone
This was an actual experiment carried out by researchers over a three-year period. This experiment taught scientists (and pet owners) something important: Animal rights advocates have argued for years about whether mice running on wheels in their cages is a sign of stress or neurotic behavior brought about by living in a confined space. But as this study would indicate, there are many different species of woodland creatures that are naturally curious and seek out activities to satisfy their curiosity (and for their pure enjoyment). The study, which observed more than 200,000 animals over a three year period, confirmed that mice sought out the running wheel for fun, sometimes multiple times a day. The researcher’s cameras also caught shrews, rats, frogs, and even slugs taking a turn on the wheel as well
An incredible technology designed for a bakery is now helping doctors distinguish cancerous cells from normal cells. Here’s the story: About fifteen years ago, market research for Japanese bakeries determined that the more variety of pastries bakeries have, the more they sell. Also, customers prefer them unwrapped. (Wrapped = preserved and unwrapped = fresh.) No packaging, however, means no barcodes to scan, which is a logistical nightmare for cashiers. Given this research, one bakery chain owner approached an engineering team in 2007 and asked for a system to automate the checkout process so they could easily sell pastries without barcodes. It took them five years – but they did it! The team developed a highly specialized AI (called BakeryScan) that can look at a pile of pastries and ID everything, tally it up, and charge the customer correctly. In 2017, a doctor saw an ad for this bakery scanning system. It occurred to him that cells under a microscope don’t look all that different from loaves of bread. And if you have a system that can differentiate a donut from a croissant – couldn’t you program it to tell the difference between normal cells and cancer cells? (Spoiler: yes, you can!)
Dr. James Barry was a transgender surgeon born in Ireland in 1789 under the name Margaret Ann Bulkey. Although raised as a girl, Bulkey made it clear that he wanted to live as a man, at one point chastising his brother by saying, “Were I not a girl, I would be a soldier!” When Margaret’s uncle, James Barry, died, Margaret adopted his name, enrolled in medical school, and started a military career as a Hospital Assistant in the British Army. Barry moved quickly through the ranks and traveled the world practicing medicine. A skilled surgeon, he became known as the first British surgeon to perform a successful cesarean section — one where both the baby and the mother survived. Barry treated everyone in his practice, no matter where he was in the world, and tended to the poor and rich alike. Barry was also an open social reformer and spoke out against unsanitary conditions in prisons and asylums. When Barry died of dysentary in 1865, his last wishes were to be buried in the clothes he died in, without his body being washed. His wishes were disrespected, however, and when a nurse undressed his body she discovered Barry’s female anatomy. Barry’s doctor, who signed the death certificate, wrote in a letter to the General Register Office that it was “none of my business” whether Barry was a man or woman — and so Barry has gone down in history as simply one of the most skilled male surgeons in medical history.
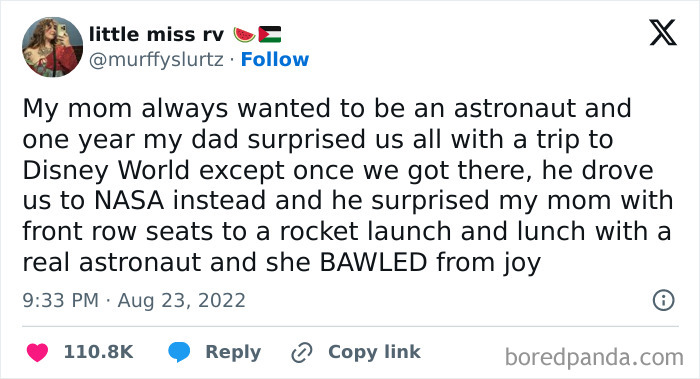
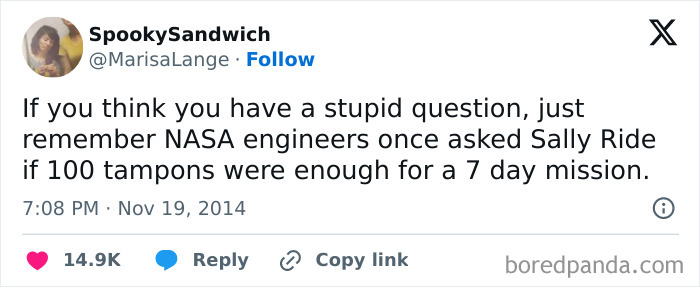
In 1983, NASA was preparing to send astronaut Sally Ride into space for a week-long trip. (“Just to be safe,” they allegedly told her.) Engineers asked Ride “Is 100 the right number?” “That would not be the right number,” Ride said. Just another reason why we need to support women in STEM careers!
A 13-year-old Belgian boy has been cured of a deadly brain cancer for the first time in history, scientists say. The boy, known as Lucas, was diagnosed at age 6 with a rare and especially deadly cancer called brainstem glioma, or Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma (DIPG). Most children diagnosed with DIPG do not live more than a year beyond diagnosis, and one recent study found that only 10 percent of children diagnosed with DIPG were alive two years after their diagnosis. Lucas was part of a clinical trial for the medication everolimus, a chemotherapy medication that blocks a protein that helps cancer cells divide and grow. Everolimus has been used in the past to treat kidney, pancreas, breast, and other types of brain cancer. The trial in which Lucas was a part of, called BIOMEDE, was testing Everolimus as a treatment for DIPG. ‘Over a series of MRI scans, I watched as the tumor completely disappeared,’ his doctor, Jacques Grill, head of the brain tumor program at the Gustave Roussy cancer center in Paris, told AFP. Lucas’ tumor was the only one in the clinical trial that completely disappeared, according to a writeup in the Daily Mail. However, seven other children in the trial have been considered “long responders” to the medication, meaning that they’ve had no relapses for at least three years after their diagnosis
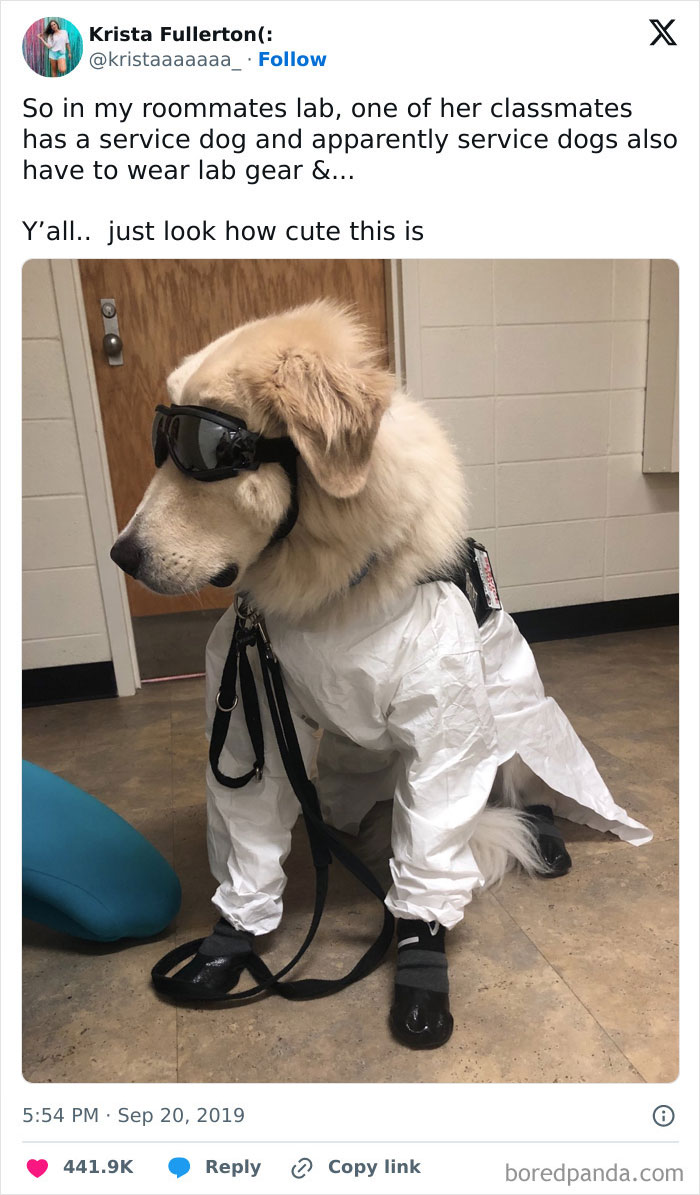
Just like humans, dogs can cry tears of joy when reunited with people they love, according to a new study in the journal Current Biology. Researchers had previously found that dogs exhibit an increase in oxytocin levels when they interact with their owners (oxytocin being a hormone associated with love, affection, and bonding). In this new study, the same researchers wondered whether dogs, influenced by oxytocin, would be an emotional event for dogs, marked by tear production. The researchers measured the dogs’ tears when reunited with their owners after several hours apart, and compared their tear production to being reunited with someone they knew but who wasn’t their owner. The scientists found that when the dogs in the study were reunited with their owner, the dogs experienced a surge in oxytocin, followed by significant tear production—much more so than when they were reunited with other human acquaintances. While a worthwhile study, this just confirms what we already knew—dogs know and love their owners (and we totally don’t deserve them)
While most of the birth control on the market is hormonal or barrier-based, scientists have recently created a method of birth control using sperm-killing antibodies that trap and kill sperm before they have a chance to fertilize. The method has been able to kill 99.9% of sperm when tested in animal models, and scientists are hopeful that it could potentially be used as a human contraceptive, via a vaginal film or ring, at some point in the future. CORRECTION: The anti-serm antibodies do not necessarily kill sperm. Instead, the antibodies clump sperm into clusters that are immobilized in the mucus and are rendered unable to reach the egg for fertilization
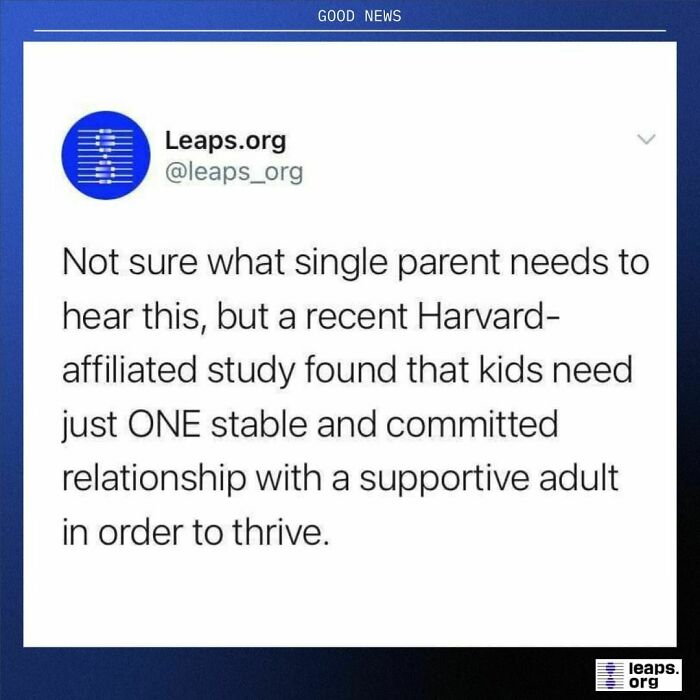
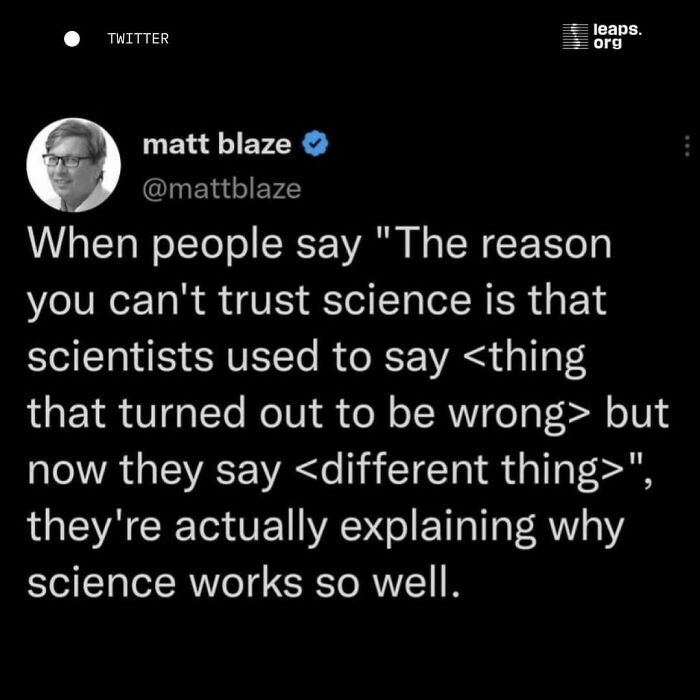
Reminder that scientific consensus can change over time as our research grows and our knowledge evolves (and we think that’s a beautiful thing)
A 14-year-old San Diego high school student has recently been named America’s Top Young Scientist for her work on a landmark new invention—headphones that play music and treat ear infections while doing so. So how do they work? Instead of using antibiotics, Fan’s headphones (named Finsen headphones) use blue light therapy to eradicate bacteria that causes mid-ear infections. Fan says she got the inspiration for her project (as well as inspiration for the name) from Niels Finsen, who won the Nobel Prize in 1903 for inventing light therapy to help treat tuberculosis

 Dark Mode
Dark Mode 

 No fees, cancel anytime
No fees, cancel anytime