Before printing presses, before paper itself, humans found ways to preserve their thoughts, beliefs, and stories on everything from clay tablets to papyrus scrolls and carefully prepared animal skins. These ancient manuscripts represent the earliest surviving thoughts of our ancestors—fragile threads connecting us directly to minds that puzzled over the same eternal questions thousands of years ago. Some contain familiar religious texts in their earliest known forms, others record mundane business transactions or astronomical observations that reveal sophisticated understanding of the heavens.
Many required painstaking restoration and translation by generations of scholars before yielding their secrets. Whether created by ancient Egyptian scribes, medieval monks, or Mayan priests, these 26 remarkable survivors have endured centuries of war, weather, and neglect to reach us today. Each time-worn page offers a humbling reminder that despite our technological advances, the human desire to record and transmit knowledge remains unchanged across millennia.
This post may include affiliate links.
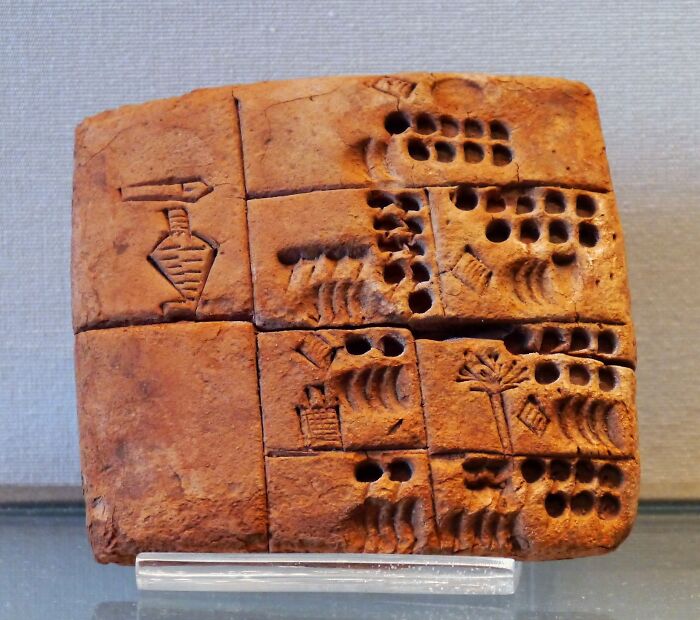
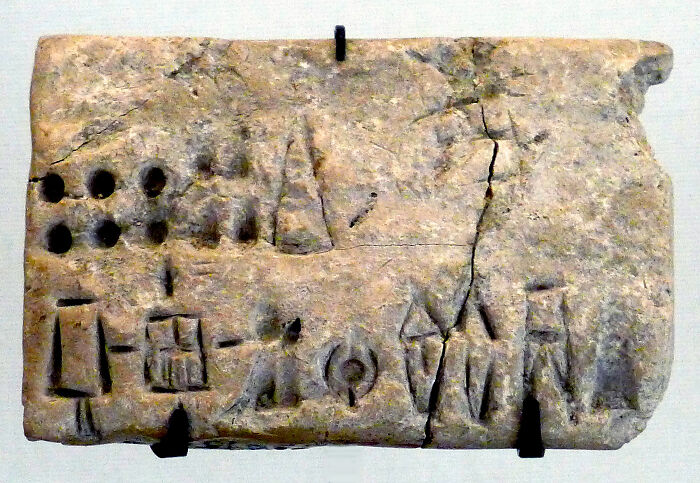
Complaint Tablet To Ea-Nāṣir
This clay tablet is basically the world’s oldest recorded customer complaint. It dates back to around 1750 BCE in ancient Mesopotamia and was written by a guy named Nanni, who was not happy with a copper merchant named Ea-nāṣir. Nanni complains about getting low-quality copper and rude service—and even says he’ll never do business with Ea-nāṣir again. A 4,000-year-old bad review!
Hittite Inscriptions
Hittite inscriptions are ancient texts written in the language of the Hittite Empire, which thrived around 1600–1200 BCE in Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). Found on stone monuments, tablets, and seals, these inscriptions offer insights into Hittite laws, treaties, and royal decrees. They are some of the earliest Indo-European writings and have been crucial in understanding Hittite society and its relations with neighboring cultures.
Kushim (Uruk Period)
Kushim is one of the earliest known names ever recorded in writing, dating back to the Uruk period in ancient Mesopotamia, around 3400–3000 BCE. His name appears on clay tablets used for accounting, specifically tracking grain transactions. Some historians think Kushim might’ve been a scribe or an official—possibly even just a job title—but either way, he's part of the very beginning of written history.
Istanbul 2461
Istanbul 2461 is a clay tablet from around 2500 BCE that shows a rare image of a Sumerian ruler—likely King Urukagina—standing before a god. It’s one of the earliest known depictions of a king being granted power by a deity. Found in the ancient city of Girsu, the tablet blends early art, politics, and religion all in one powerful scene.
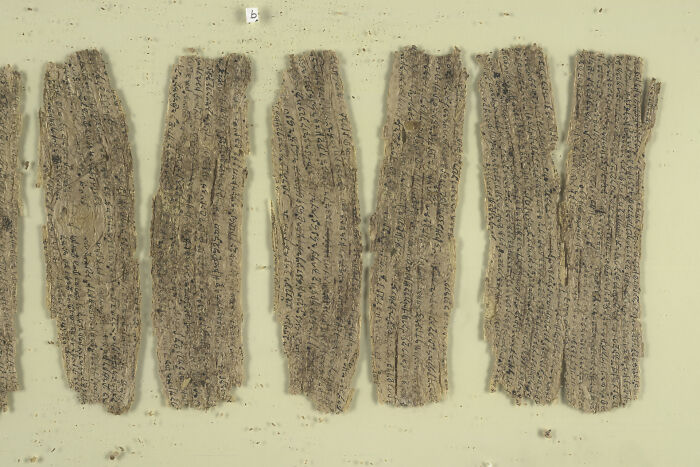
Gandhāran Buddhist Texts
The Gandhāran Buddhist texts are some of the oldest surviving Buddhist manuscripts, dating back to the 1st century CE. Written on birch bark in the ancient Gāndhārī language, they were found in modern-day Pakistan and Afghanistan. These texts offer early versions of Buddhist teachings and show how Buddhism spread and evolved across regions. They're a major find for scholars of ancient religion.
Oracle Bone Script
The Oracle Bone Script, dating back to around 1200 BCE during China’s Shang Dynasty, is the earliest known form of Chinese writing. It was inscribed on animal bones and turtle shells, used in divination practices. These inscriptions record royal inquiries to ancestors and gods about matters like weather, warfare, and harvests. It’s a key piece in understanding the origins of Chinese characters and ancient Chinese culture.
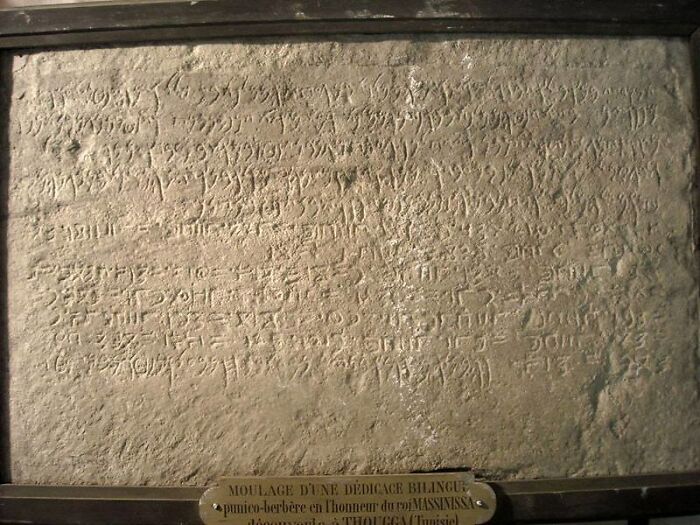
Temple (Massinissa) Inscription
The Temple of Massinissa inscription, found in modern-day Algeria, dates back to around the 2nd century BCE. It commemorates King Massinissa, the ruler of the ancient Berber kingdom of Numidia, and his contributions to the region. The inscription honors his building of temples and his loyalty to Rome, reflecting the political and religious influences during his reign. It’s an important artifact for understanding Numidian history and its interactions with Rome.
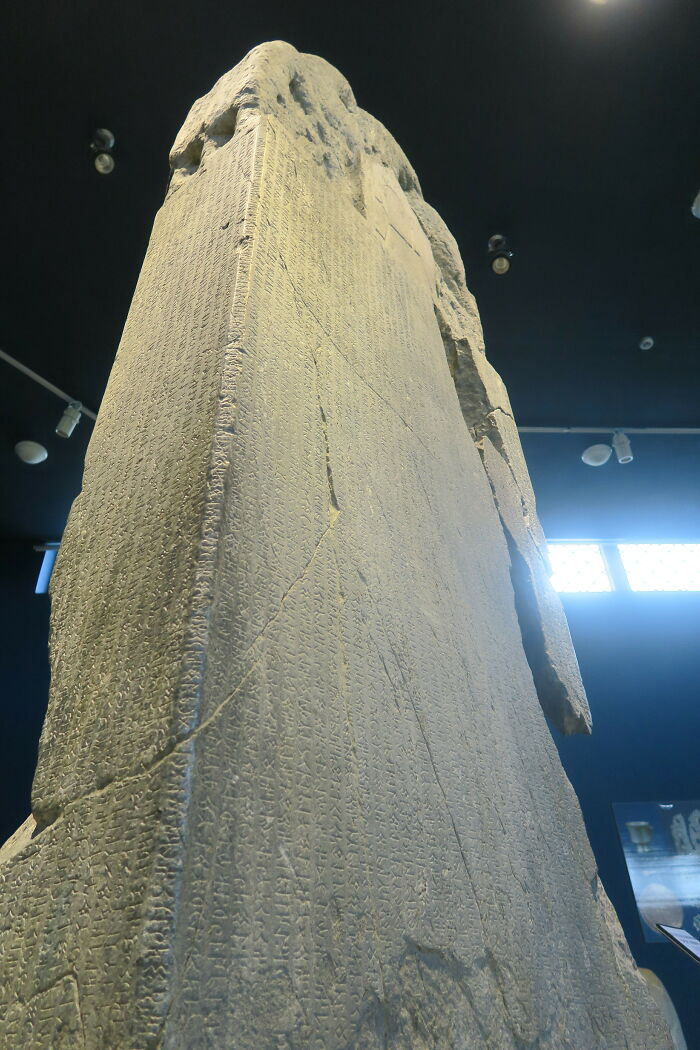
Orkhon Inscriptions
The Orkhon inscriptions, dating back to the 8th century CE, are the earliest known examples of written Turkic languages. Found in the Orkhon Valley of Mongolia, these inscriptions commemorate the deeds of the Gokturk Khaganate rulers, particularly Bilge Khagan and his brother Kül Tigin. The texts are written in Old Turkic script and provide crucial historical information about the political, military, and cultural life of early Turkic peoples.
Memorial For Yelü Yanning
The Memorial for Yelü Yanning, created in 986 CE, is the earliest known Khitan inscription of significant length. It honors the military leader of the Khitan-led Liao dynasty and features both Khitan script and Chinese. The inscription celebrates his achievements and provides valuable insights into the Khitan language and script, offering a glimpse into early Khitan culture.
Kiev Missal
The Kiev Missal, dating back to the 11th century, is one of the oldest known liturgical manuscripts in the Slavic tradition. Written in Old Church Slavonic, it contains Christian prayers, hymns, and rituals used during the Divine Liturgy. This manuscript is significant not only for its religious content but also for its insights into early Eastern Slavic art and calligraphy.
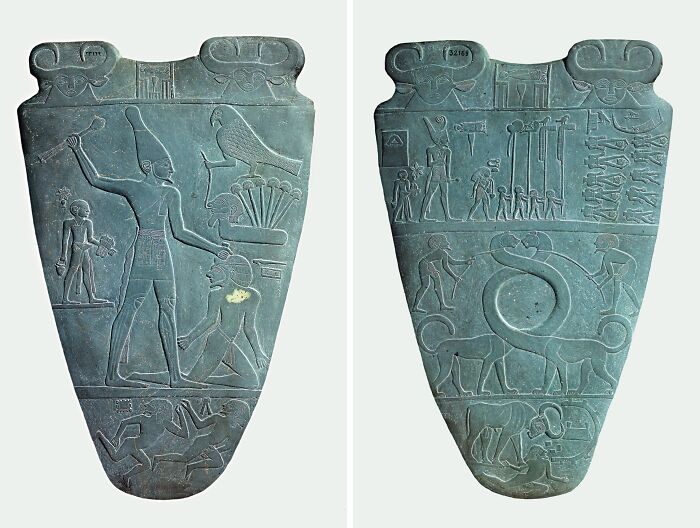
Narmer Palette
The Narmer Palette is an ancient Egyptian artifact dating back to around 3100 BCE, and it’s a huge deal in history. It shows King Narmer wearing both the white and red crowns, symbolizing his unification of Upper and Lower Egypt. The palette was likely ceremonial, not for everyday use, and features some of the earliest examples of Egyptian hieroglyphs.
Palermo Stone
The Palermo Stone is one of the oldest historical records from ancient Egypt, dating back to around 2500 BCE. It’s a black basalt slab that lists kings from early dynasties and records major events year by year—like Nile flood levels, festivals, and royal decrees. It gives historians a rare glimpse into Egypt’s earliest rulers and how they documented their reigns.
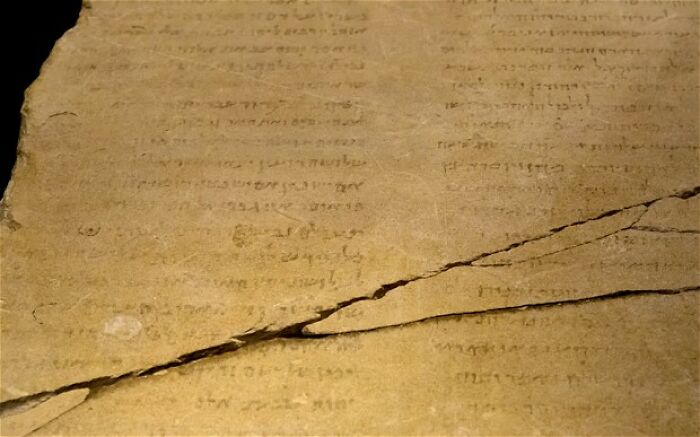
Dead Sea Scroll
The Dead Sea Scrolls are a collection of ancient Jewish texts discovered in caves near the Dead Sea between 1947 and 1956. Dating from around 200 BCE to 100 CE, they include some of the oldest known copies of the Hebrew Bible, along with other religious writings. These scrolls offer a rare look into Jewish beliefs, practices, and daily life over 2,000 years ago.
Nash Papyrus
The Nash Papyrus is one of the oldest known fragments of the Hebrew Bible, dating back to around 150–100 BCE. Discovered in Egypt, it contains parts of the Ten Commandments and the Shema prayer. Before the Dead Sea Scrolls were found, this was the oldest known biblical text. It’s a key piece in understanding how ancient scriptures were preserved.
Gabriel's Revelation
Gabriel’s Revelation, also called the “Jeselsohn Stone,” is a 1st-century BCE Hebrew inscription written on stone rather than scroll. It features an apocalyptic message supposedly delivered by the angel Gabriel. Some scholars believe it hints at a messianic figure who would rise from the dead after three days—sparking big debates about its possible connection to early Christian ideas.
Proto-Elamite Script
The Proto-Elamite script, used around 3200–2700 BCE in ancient Elam (modern-day Iran), is one of the earliest undeciphered writing systems. Found on clay tablets, it’s believed to be an early form of writing, possibly used for administrative purposes. While it predates the more famous cuneiform script, scholars are still working to crack its code and understand its full significance.
Mesha Stele
The Mesha Stele, dating to around 840 BCE, is a large stone monument from the ancient kingdom of Moab (modern-day Jordan). It records King Mesha's victories over Israel and details his military campaigns, as well as his efforts to build and restore Moabite cities and temples. The stele is significant for its historical and biblical connections, providing evidence of events mentioned in the Old Testament.
Bir El Qutt Inscriptions
The Bir el Qutt inscriptions, discovered in Algeria, date back to the 1st century BCE and are written in the ancient Libyco-Berber script. These inscriptions are believed to be related to local religious practices and may have served as dedications or commemorations of important events. They offer valuable insights into the early cultures of North Africa and their interactions with the Roman Empire.
Humac Tablet
The Humac Tablet, dating to around the 4th century CE, is an ancient stone inscription found in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is written in the Latin alphabet and is considered one of the earliest examples of the Bosnian language. The tablet contains a Christian inscription, providing insights into early Christianity in the region and the development of the Latin script in South Slavic areas.
Cantar De Mio Cid
The Cantar de mio Cid (Song of my Cid) is an epic Spanish poem from the 12th century, one of the oldest and most important works in Spanish literature. It tells the story of Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar, known as El Cid, a nobleman and warrior who fought in the Reconquista. The poem highlights his bravery, loyalty, and exile, offering insights into medieval Spanish culture, heroism, and the complex relationship between Christians and Moors.
Västgötalagen
The Västgötalagen (Law of Västgötaland) is a medieval Swedish law code from the 13th century. It governed the province of Västergötland and is one of the oldest surviving Swedish legal texts. Written in Old Swedish, it provides a glimpse into early Swedish society, covering topics like land ownership, marriage, and crime. The law highlights the role of local courts and customary law in shaping medieval Scandinavian justice.
Neacșu's Letter
Neacșu's Letter, written in 1521, is the oldest known document in the Romanian language. It was sent by Neacșu of Câmpulung, a merchant, to Hans Benkner, a Saxon trader in Kronstadt (Brașov). The letter discusses the political situation in the region and serves as an important artifact for the development of the Romanian language and early communications in the Balkans. It is notable for its mixture of Old Slavonic and Romanian language influences.
Edicts Of Ashoka
The Edicts of Ashoka are a series of inscriptions carved on rocks and pillars across India during the reign of Emperor Ashoka (268–232 BCE). These edicts promote moral and ethical teachings based on Buddhism, such as non-violence, respect for all religions, and social welfare. They are a key source for understanding Ashoka’s transformation from a ruthless conqueror to a proponent of peace and dharma.
Placiti Cassinesi
The Placiti Cassinesi are a set of medieval legal documents from the 8th to 9th centuries, written in Latin, and found in the Abbey of Monte Cassino in Italy. These records mostly deal with land transactions and disputes between the abbey and local aristocrats. They are significant for their historical insight into early medieval Italian society and the relationship between the church and the nobility. The documents also provide one of the first instances of the use of the Neapolitan dialect in writing.
Freising Manuscripts
The Freising Manuscripts, dating back to the 10th century, are a set of Old Church Slavonic texts written in Glagolitic script. They contain religious writings, including prayers and hymns, and are among the earliest examples of Slavic literature. These manuscripts are significant for their role in the spread of Christianity in Slavic-speaking regions and for their unique insights into early Slavic language and script.
Huarochirí Manuscript
The Huarochirí Manuscript, dating back to the early 17th century, is an important text from the Andean region of Peru. Written in Spanish and Quechua, it contains a collection of myths, rituals, and religious beliefs of the Huarochirí people. This manuscript offers valuable insights into pre-Columbian Andean culture and their adaptation to Spanish colonial influence, showcasing a blend of indigenous traditions and Christian elements.

 Dark Mode
Dark Mode 

 No fees, cancel anytime
No fees, cancel anytime